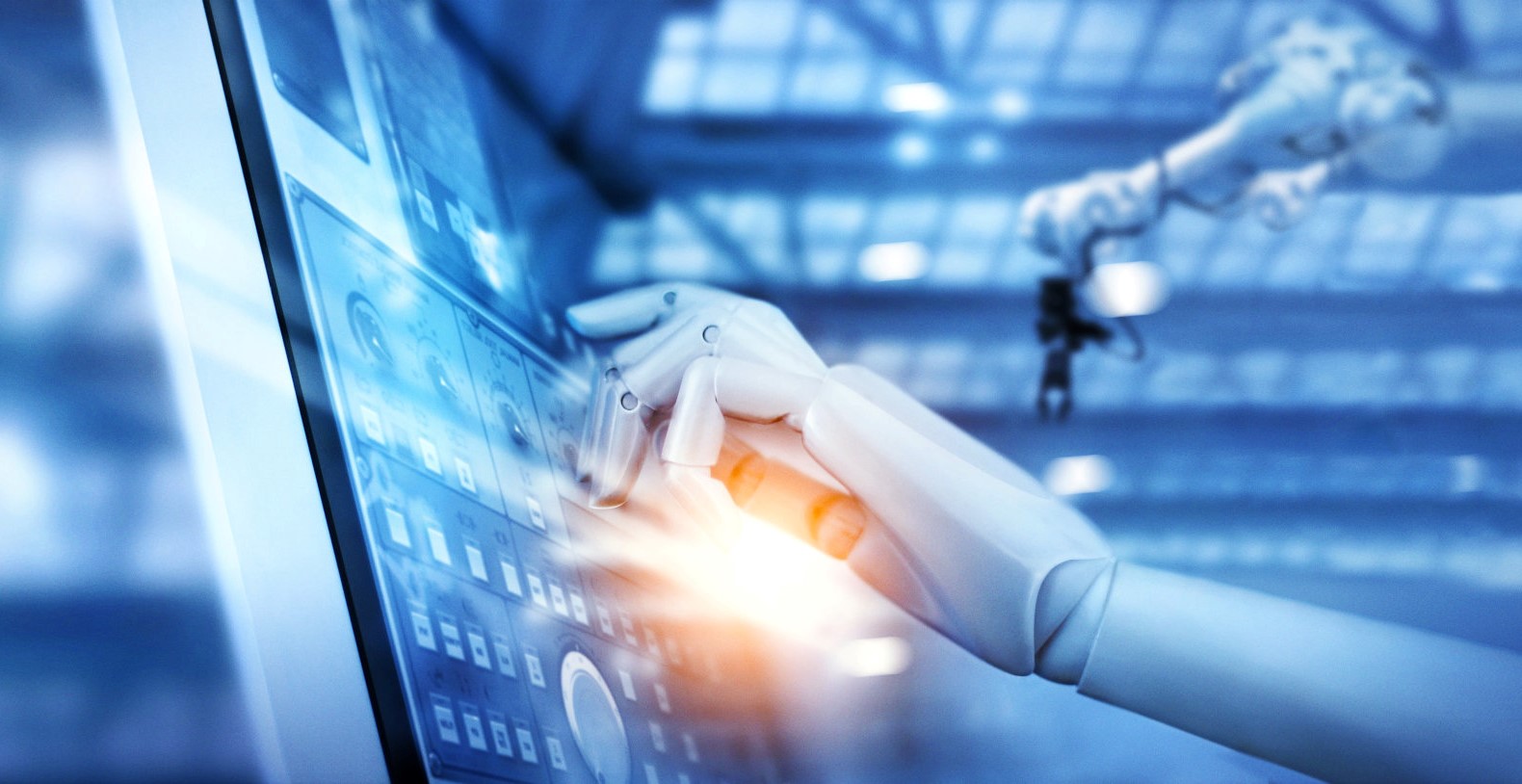
Digitalization and automation characterize modern smart factories. As a pioneer, Leadec is breaking new ground here, developing and realizing appropriate solutions to make manufacturing fit for Industry 4.0.
Production IT
The networking of production and the integration of cloud systems help companies to better understand their production and to recognize potential. With our extensive range of Production IT, we give our customers all the tools they need in connection with their know-how to optimize their production by providing data. Based on the information compiled in the data lake, all processes can be digitally displayed and analyzed. The results can e.g. reduce downtime and manufacturing costs.
We enable the targeted control of your entire value-added process as well as a fast and flexible ability to react to necessary changes.